Topics
Commenced Development of Antenna Circuit Substrates Using Quartz-Glass Bonded Wafers for Higher Precision In- vehicle Radar
Contributing to Passenger Safety and Convenience in Vehicles
September 01, 2025
NGK INSULATORS, LTD. (hereinafter “NGK”) and the Fraunhofer Gesellschaft (FHG-IZM (located in Berlin, Germany; hereinafter “FHG-IZM”) and Fraunhofer Gesellschaft -FHR (located in Wachtberg, Germany; hereinafter “FHG-FHR”)), a German research institute in the field of science and technology, started the joint development of antenna circuit substrates for In-vehicle radar using quartz-glass bonded wafers made by NGK.
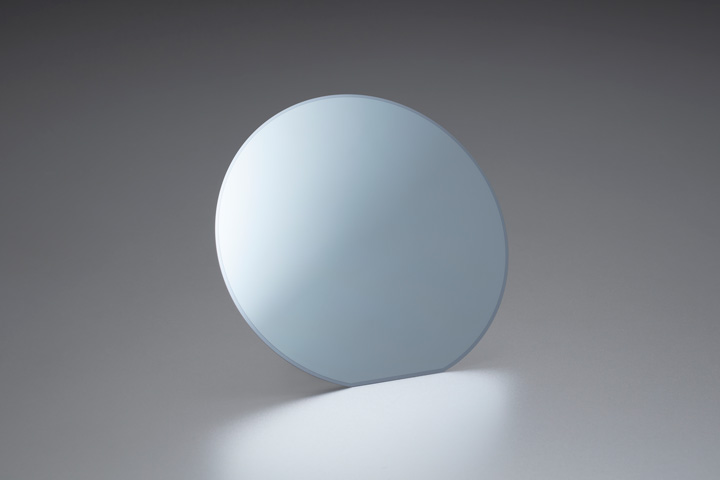

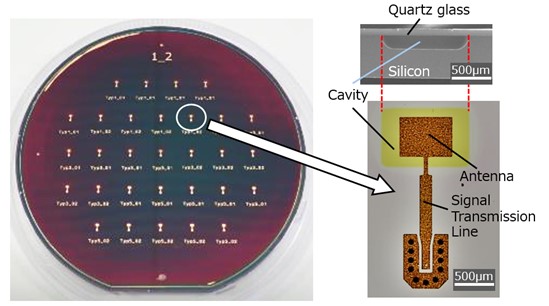
In 2024, NGK and FHG-IZM developed an antenna circuit substrates for 6G wireless communications using sub-terahertz waves*1, which are suitable for high-speed communications. This development used quartz-glass bonded wafers with cavities to verify the basic performance of an antenna circuit substrates for a wide frequency band of sub-terahertz waves (patent pending).
This time, based on the results of the previous development, NGK and FHG-IZM will apply quartz-glass bonded wafers to develop an antenna circuit substrates optimized for automotive radar. A radar module using the substrates and dedicated high-frequency integrated circuit*2 will be designed and prototyped at FHG-FHR, and verification of the radar’s basic performance is scheduled to be completed by November 2025.
NGK’s bonded wafers are electronic device wafers made by bonding different materials together using innovative direct-bonding and precision-polishing technologies. Quartz-glass bonded wafers are combinations of quartz-glass and silicon wafers bonded together. They combine quartz’s low-loss performance for electromagnetic waves and the silicon base material’s superior heat dissipation properties.
As “CASE” (Connected, Autonomous, Shared, Electric) advances worldwide in the automobile industry, demand is increasing for radar inside vehicles that detects passengers’ vital signs and gestures. The use of sub-terahertz waves is being considered to enhance the precision of radar, but sub-terahertz wave transmission and reception generate significant heat in the transceiver circuit (radio frequency integrated circuit) mounted on the antenna circuit substrates, which lowers the sensing accuracy. However, applying a quartz-glass bonded wafer with cavities to the antenna circuit substrates improves the efficiency of radio wave transmission and reception and the heat dissipation of the transceiver circuit, thereby contributing to higher accuracy of radar detection.
-
*1Sub-terahertz waves: Radio waves with a very high frequency of 100 gigahertz to 300 gigahertz suitable for high-speed communications
- *2High-frequency integrated circuit: A semiconductor device designed to transmit, receive, and process radar signals
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
Founded in 1949, the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is Europe’s largest application-oriented research organization in the field of science and technology. With 76 research institutes throughout Germany and offices in Europe, the Americas, and Asia, the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft offers a wide range of services, including contract research, joint research, consulting, and workshops, to meet the needs of industry. It conducts practical applied research for the benefit of private companies, public institutions, and society as a whole.
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
