Research Development
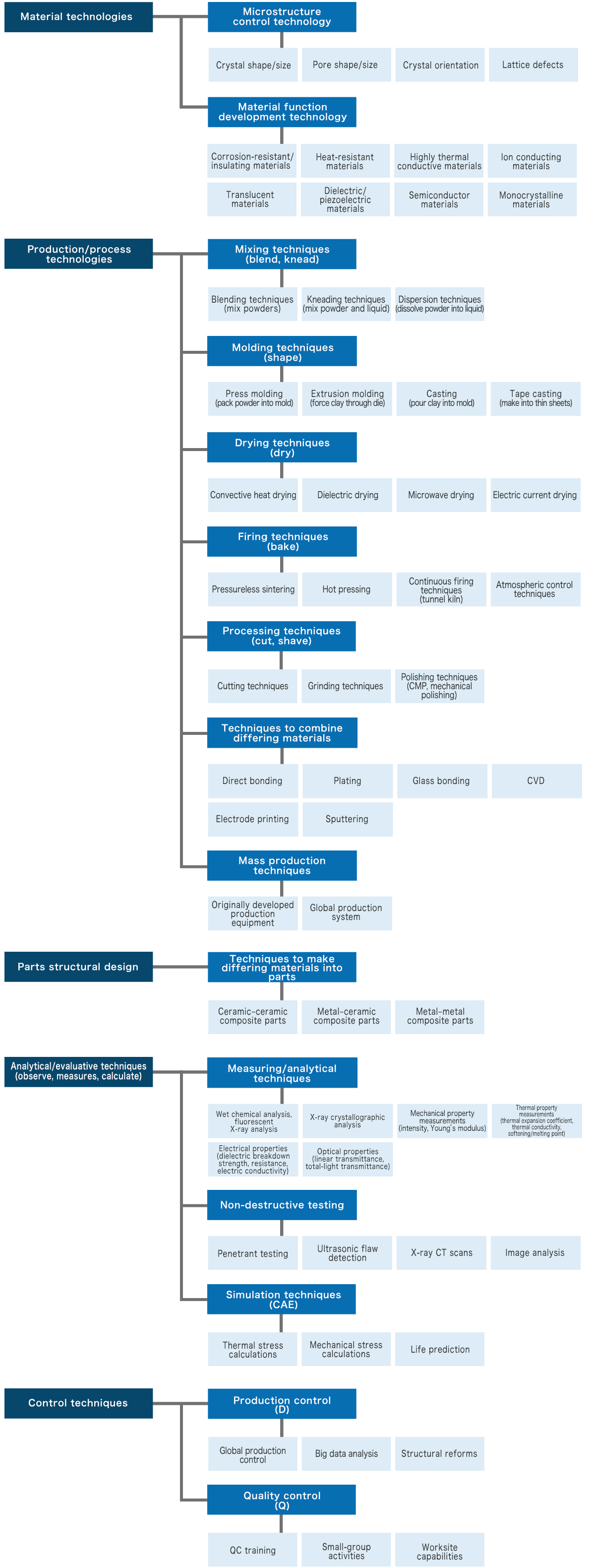
The NGK Group's Core Technologies
Competitive Strength
Producing ceramics is like putting together a complex jigsaw puzzle
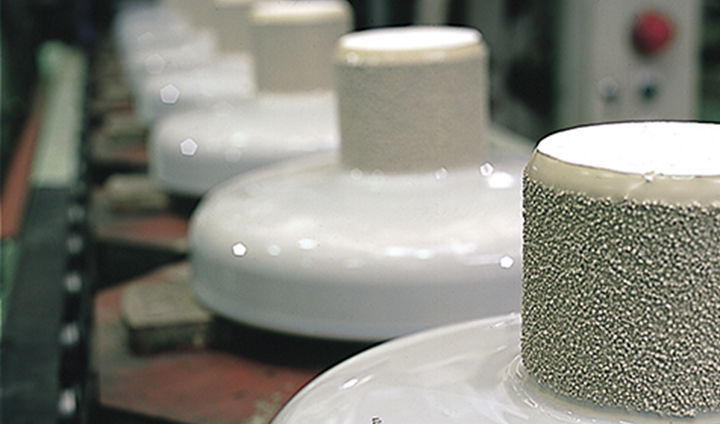

From its very beginning, the NGK Group has sought to reexamine conventional ceramic manufacturing practices in light of the latest science and technologies in order to help it identify the optimal combination of process conditions for each of its products. And after nearly 100 years, this pursuit of optimization has accrued a wealth of technology and expertise from which the NGK Group draws its competitive strength.
Three Stages Forming Ceramic Products
-
- 01SSelecting and mixing the raw materials on which the product is based
: Blending and kneading - 02Molding the product
: Shaping - 03Firing the product so as to realize the optimal crystalline structure
: Baking
- 01SSelecting and mixing the raw materials on which the product is based
-
Ceramic manufacturing is patient, methodical work, which requires you to blow life into inanimate material that is hard and brittle.
There are three stages by which raw materials become products, and each requires advanced technologies.
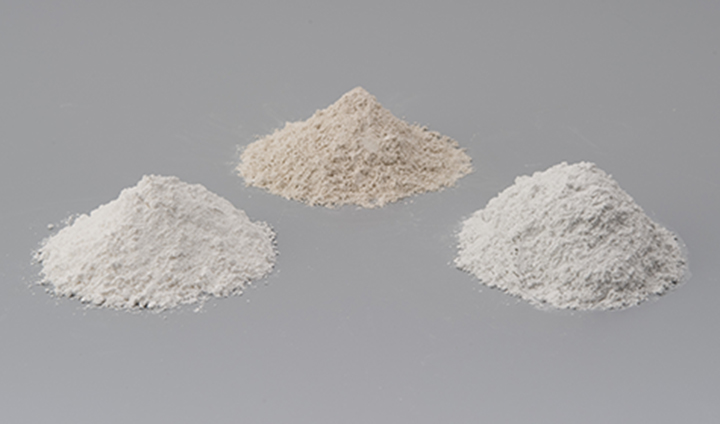

Particles of the powdered raw materials that form ceramics have a diameter of just 1/1,000 of a millimeter. If the particles are too large, it will take too long to fire them, and if they are too small, they will exhibit cracking and variability. If particles of different sizes are mixed together, distortion may result. The optimal raw materials must be chosen from tens of thousands of possibilities and blended together.
The blended raw materials are molded using a method that suits the shape of the product and fired in a kiln. Upon firing, the particles of raw materials fuse together and contract, causing finished products to shrink by about 25% for insulators and about 10% for HONEYCERAM. The key priority is to create uniform, appropriate gaps between powder particles during the molding stage. Failure to do so will result in variability in how the product shrinks when fired, causing its shape to change. Conditions inside the kiln are also important. The powdered raw materials harden to create minuscule crystals, and the structure of these crystals determines a ceramic product’s characteristics. That crystallization process is influenced by the temperature and duration of the firing process, flame color (radiant temperature), and surroundings (water vapor partial pressure inside the kiln). If temperature variations inside the kiln create differences in how firing proceeds, the finished product will not be uniform.
In this way, high-performance ceramic products can only be produced if a variety of conditions are satisfied at every stage of manufacture. It is like a complex jigsaw puzzle. The breadth of accumulated technologies and expertise is the source of the NGK Group’s competitive strength.
To realize the NGK Group Vision, we carry out groundbreaking research and development and create innovative technologies in the shortest time possible by combining our accumulated strengths with state-of-the-art technologies such as Digital Transformation (DX).
Core Technologies of the NGK Group