Sustainable, innovative, and resilient:
How ceramics are shaping an ideal world
This content is produced in partnership with CNN International Commercial.
The world is at a pivotal moment in the fight against climate change, where even the smallest action could have the biggest impact. Discover the advanced ceramic technologies that are working to clean the atmosphere, power our cities, and preserve society.
Innovate to Accelerate
As the climate emergency intensifies, so too does the urgency to do something about it. The actions we take now could bring us closer to a more connected future-where technology is the enabler of renewable energy consumption, autonomous and zero-emission transport, and ultra-smart cities.
But to achieve this net-zero reality by 2050, the International Energy Agency (IAE) says annual clean energy investment worldwide will need to more than triple by 2030 to around ¥540 trillion ($4 trillion), especially with almost half of the reductions in CO2 emissions relying on the technologies currently in the prototype phase.
One company accelerating its innovation efforts to bring these technologies to market in time is one of the world’s leading manufacturers of ceramics: NGK Insulators (NGK).
From Energy and Mobility to the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry, NGK is developing cutting-edge and environmentally-forward solutions for some of the most progressive business areas. To understand how the company found its niche, President at NGK, Shigeru Kobayashi, reveals the surprising power of ceramics and how they are now helping to shape a carbon-neutral and digital-first world.
Restoring Balance
Replacing fossil fuels with renewable sources is crucial to achieving carbon neutrality and energy efficiency. However, generating electricity from solar panels and wind turbines relies on an unreliable supply of sun and wind. Realizing the power of storage batteries in stabilizing renewable energy, NGK put its large-capacity, high-energy-density, long-life storage NAS* batteries to use as part of a world-first application.
Twenty years on, they are continuing to transform the potential of renewable energy. By supplying high-output power for long periods of time, storing surplus energy from periods of high solar and wind activity, and regulating energy flow to the grid, NAS batteries enable a constant, uninterrupted, and reliable power supply.
As global deployment increases, they stand to become a core component in the shaping of ‘A Supercharged Greener Future ,’ where sophisticated battery systems and renewable energy sources work together to realize a carbon-neutral society.
“These batteries will provide great contributions as an indispensable technology for the stable power supply and effective utilization of renewable energy.”
Shigeru Kobayashi, President, NGK
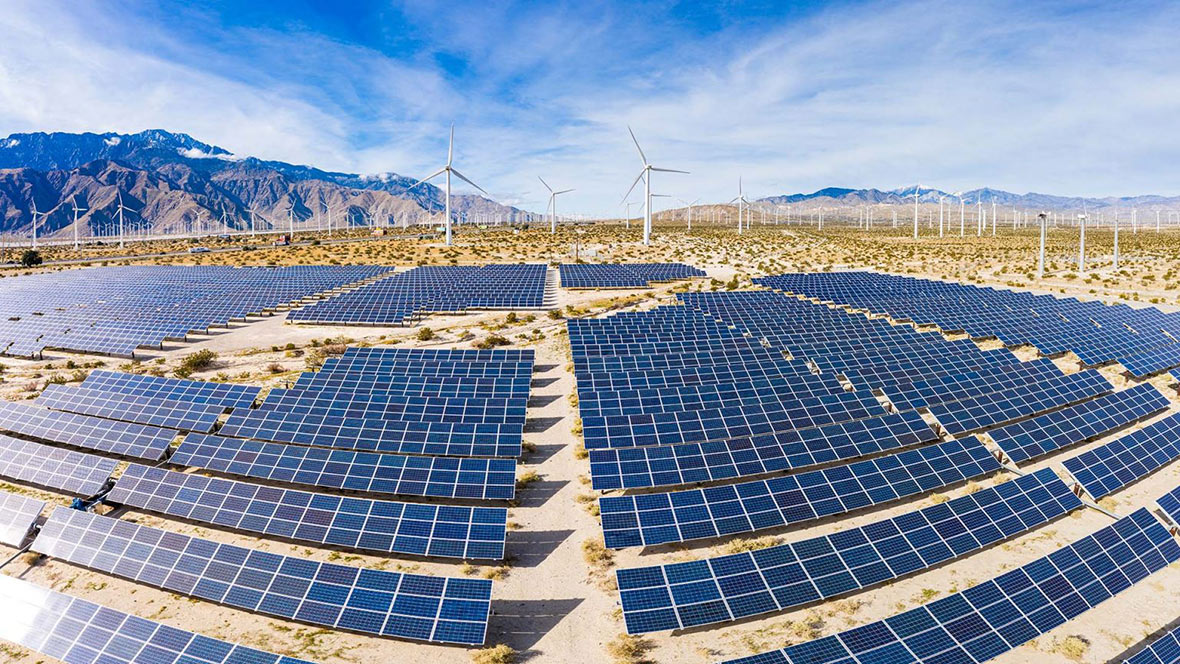

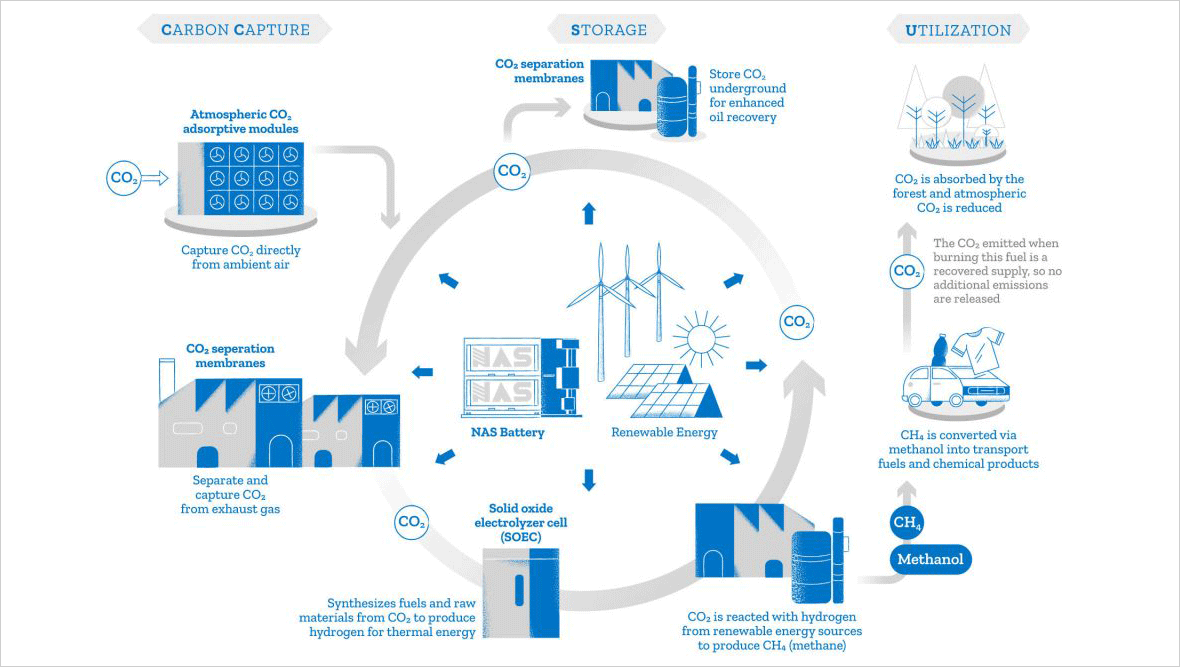
While renewable energy reduces carbon emissions, there is still the challenge of capturing carbon, which is where “carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) is a key factor,” says Kobayashi. Subnano-ceramic membranes from NGK separate and capture CO2 with high precision and stability at the molecular level using proprietary sub-nanometer-sized pore control technology.
Subnano-ceramic membranes are effective in separating and recovering CO2 and methane from industrial exhaust gases, even in the harshest of environments where preexisting technologies cannot be implemented. But their value doesn’t end there: there are hopes that this technology will someday cover all aspects of the carbon cycle. For example, the company is advancing the application of this technology to a reactor for efficiently generating synthetic fuels. It will work by combining recovered CO2 with hydrogen from renewable energy sources, which is expected to further contribute to the shift toward a carbon-neutral society.
Powering Connectivity
Sustainable by design and innovative by nature, NGK ultimately aims to use its “unique ceramic technology to contribute to future energy, environmental protection, and industrial development, and to help people around the world live a happy, comfortable life,” explains Kobayashi. Digitalization is a significant part of this, allowing everyone to make the most of new opportunities in connectivity and communication.
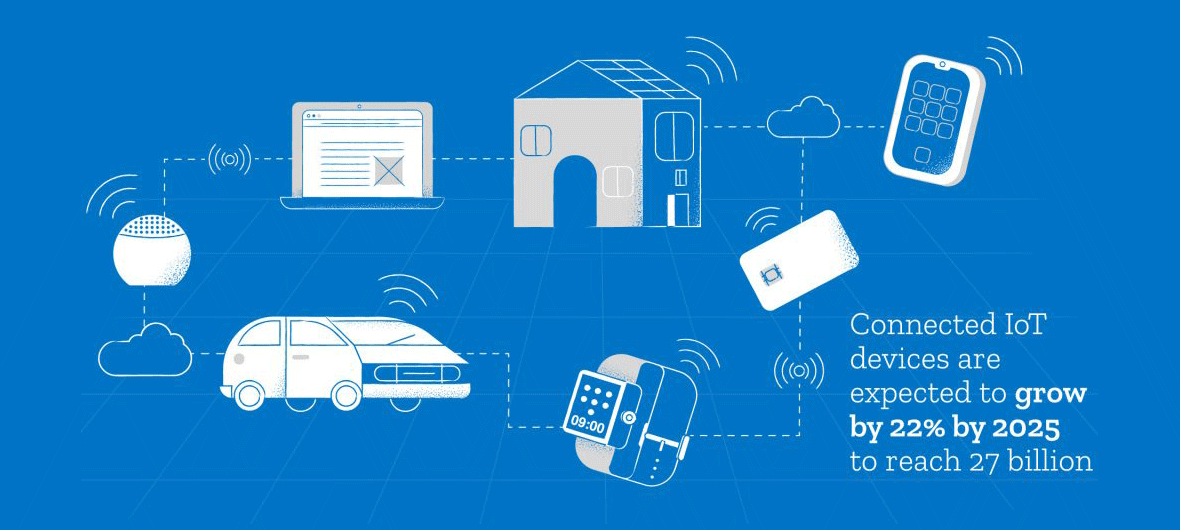
EnerCera* ultra-thin, lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, for instance, are revolutionizing the capabilities of IoT. It’s technologies like these that are working behind the scenes to power our lives with controlled wireless connectivity, often without us even knowing.
They may be small, but EnerCera batteries have 50-100% higher power capacity than conventional rechargeable batteries. This means they can be inputted into smart cards, wearable devices, and electronic price tags for a maintenance-free IoT experience that works smarter and for longer.
Like these wireless devices, which would be obsolete without the appropriate batteries to power them, the next generation of high-speed communication would be inconceivable without the technology to back it.
Wafers from NGK represent just one of the many ceramics-based innovations contributing to the digital transformation of society. Low dislocation density Gallium Nitride (GaN) wafers—produced by NGK’s proprietary liquid phase crystal growth method—improve the power and efficiency of Radio Frequency (RF) devices, while bonded wafers will contribute to future wireless and optical communication networks through unique precision-polishing and bonding technologies.

A Responsible Future
With a focus on carbon neutrality and digital society, NGK will continue to develop the sustainable solutions we need to build the world we envision. “We are looking for a recycling-oriented society, in which digitalization is promoted and people’s lives become more convenient,” says Kobayashi, and only when we “adapt ourselves to circumstances and keep taking on new challenges, new actions” will we find it.
Its ‘Road to 2050’ NGK Group Vision is a testament to this commitment, through which it has pledged a series of sustainable growth goals, including a net-zero volume of CO2 emissions by 2050. Over the next ten years, it will invest just over ¥300 billion ($2.1 billion) in research and development, with 80% allocated to achieve carbon neutrality and a digital society.
Industries can expect this investment to fund future technologies, such as solid oxide electrolysis cells, honeycomb structural reactors for synthetic fuel, and next-generation mobility sensors. Ceramics for semiconductor manufacturing equipment, meanwhile, will remain invaluable as we experience an unprecedented influx of connected devices and data distribution.
NGK’s hope is that by 2050, 80% of its sales will be generated by its two business fields: “carbon neutrality” and “digital society”—positioning the company as a technological innovator and invaluable contributor to society. It is determined to create a future where people can coexist with nature, which is why its products will endeavor to support the preservation of our social infrastructure and the environment.
* NAS and EnerCera are trademarks of NGK Insulators, Ltd., registered in the US and other countries