Digital disruption from the kiln
This content was paid for by NGK Insulators and produced in partnership with the Financial Times Commercial department.
Ceramics are enabling a smarter world in surprising ways.
In a digital society, ceramic technologies and materials will be vital for the sensors, radar, high-speed telecommunication devices and power semiconductors needed for autonomous and electrified transport. Highly compact, durable and wirelessly rechargeable ceramic-based batteries will power IoT devices everywhere, from supply chains to factory floors. And high-performance wafers and actuators using ceramic materials will play a critical role in processing the vast streams of data circulating through a digital world.
In many ways, such a world is already here. And NGK Insulators, the Japanese technology company pioneering such solutions, is stepping up to deliver this ongoing ceramic-driven digital transformation. Together with its goal of contributing to carbon neutrality, the company is determined to generate new value in changing times.
“There is no question that the current explosive growth of digital technology in our lives will continue onto 2050: more semiconductors, more data, faster telecommunications from 5G to 6G and beyond,” says Shigeru Kobayashi, NGK’s president. “For these trends, we will utilise our high-precision ceramics technologies to develop products for a carbon-neutral and digital society.”
Riding a digital wave
In fact, NGK already plays an indispensable role in digital society.
The Japanese ceramics expert is a key global supplier of ceramic components for semiconductor manufacturing equipment, piezoceramic actuators for HDD used in data centres, and bonded wafers for SAW filters that filter out unwanted smartphone frequencies. If you have a high-end smartphone, there’s a good chance it contains NGK wafers or semiconductors made using the company’s components. It may also regularly receive data processed by NGK’s actuators.
Reflecting this crucial role, NGK’s electronics and SPE (Semiconductor Production Equipment)-related business has grown rapidly over the past two decades. Its digital society business segment sales of ¥138bn (roughly a quarter of total sales of ¥579bn) for the fiscal year ending March 2024. It aims to generate over ¥300bn by 2030 for this segment by continuing to roll out unique ceramic technologies with significant impact for areas like mobility, logistics, automation, healthcare and telecommunications.
EnerCera everywhere
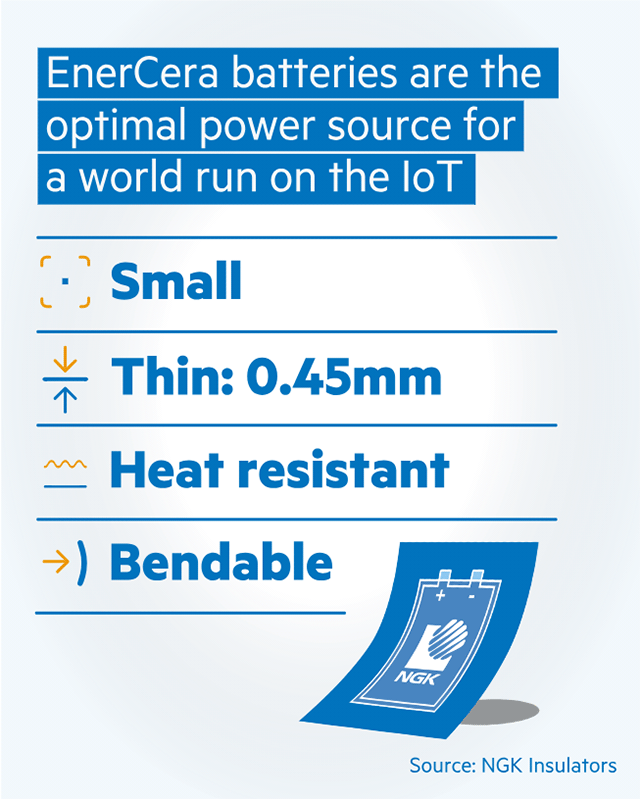
One such product that has gained worldwide acclaim is the EnerCera* battery. At only 0.45mm thick and the size of a stamp, this ground-breaking technology promises to transform the world of IoT.
Currently, most wireless IoT devices are powered by single-use batteries — with the hassle and cost of replacements — or rechargeable ones with long charging times and short lifespans. Existing batteries are also not sufficiently heat resistant, which prevents them from being installed through heat-intensive manufacturing processes and limits their use in high-temperature environments.
The EnerCera battery can overcome these bottlenecks. The battery offers high capacity, is ultra-small, ultra-thin, long-living, bendable and has a great affinity for wirelessly rechargeable technologies. These properties make it an ideal option to power maintenance-free IoT devices. Since its launch in 2019, the company has conducted numerous demonstration tests for the IoT battery, from logistics to wearables, air quality monitoring, factory automation and smart agriculture.
Manufacturers can also use flexible sensor tags powered by the EnerCera battery to monitor the environment and condition of high-quality food and drink products, such as wine shipped overseas. In the future, these sensor tags will be able to monitor additional data, such as shocks or positional changes during transport.
“There is a growing demand for traceability in logistics, particularly the need to meet standards such as Good Distribution Practices (GDP) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) for assuring quality in pharmaceutical and food distribution,” says Ryohei Iwasaki, executive vice president and head of Corporate NV (New Value) Creation for NGK.
“Since the EnerCera battery is also resistant to a wide range of temperatures, it is ideal for use in cases involving cold-chain shipments or even under direct sunlight.”
Another important feature of NGK’s new battery is its affinity for wirelessly rechargeable technologies and energy harvesting. The EnerCera’s small internal resistance means it can be charged even with weak inputs of wirelessly transmitted electricity while still delivering enough power for wireless communication.
NGK has partnered with Torex, a Japanese power-supply integrated circuit (IC) manufacturer, and OSSIA, a US leader in wireless charging technologies, to develop a wireless power transfer (WPT) system with a transmitter that can power multiple EnerCera batteries wirelessly simultaneously, even while in motion.

With wireless charging, products can be designed without needing to have easy access for frequent battery replacement and the environmental costs of disposing battery waste can be reduced. Wireless charging can also be helpful in dark factories and warehouses that do not permit photovoltaic power generation for IoT devices.
“Along with WPT systems and logistics tracking sensors, we expect the EnerCera battery to be used in conjunction with renewable energy systems, in wearables and as a backup electricity source,” says Iwasaki.
Ceramic materials unleashed
The ceramics and electricity industries have a longstanding affinity. The versatile properties of ceramic materials, such as electrical resistance, ionic conductivity, resistance to heat and corrosion and mechanical strength, allow it to be used in both batteries and insulators.
But ceramics have many more features and applications waiting to be unleashed. NGK excels at manipulating the material’s atomic-level structure, aligning its crystals, and techniques like ultra-high precision polishing and bonding. These technical applications have led to advanced ceramic materials being used in new products such as high-performance wafers and batteries.
One growth area is the use of ceramic substrates for the circuit boards of power semiconductor modules in vehicles and industrial equipment. NGK’s substrates for these power modules, have a superior ability to dissipate insulated heat against increased output. The market for these circuit substrates are expected to jump many-fold with the electrification of automobiles and increase in renewable energy applications.
The ancient, versatile material will continue to play a central role in our digital society, making our world smarter.
NAS and EnerCera are trademarks of NGK Insulators, Ltd., registered in the U.S. and other countries


