Sustainability
Information Disclosure Based on TNFD Recommendations
Introduction
What is TNFD?

The Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures is a global initiative launched in 2021 amidst an international sense of crisis about environmental degradation and the increasing importance of restoring nature. Its aim is to construct a framework for risk management and disclosure of nature-related risks by companies. The taskforce presented its recommendations in September 2023, calling for companies to be aware that nature-related issues are related to strategic risks, and encouraging companies to identify and disclose the nature-related dependencies and impacts they have through their business, as well as the accompanying risks and opportunities.
In January 2024, the NGK Group declared we would shortly begin information disclosure under the TNFD framework as an TNFD Early Adopter*1. We made our first disclosure in July 2024 and have now broadened the scope of our disclosure.
1. TNFD Early Adopter: Companies and organizations that will begin information disclosure by FY2025 (As of January 2024: 320 companies in 46 countries, 80 of them Japanese)
NGK Group Approach to Nature and Biodiversity
Our society and its economic activities depend on nature and its blessings. But nature is said to be in rapid decline worldwide due to the adverse impact of these activities. Amidst a growing sense of urgency and awareness of the importance of restoring nature, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) was adopted at the 15th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP15) in 2022. It sets a common global goal of being "nature positive," which means taking action to stop and reverse the loss of biodiversity by 2030.
In the NGK Group Environmental Vision, we set the idea of harmony with nature as one of our most important issues. And NGK aims to operate in harmony with nature by minimizing its environmental impact on ecosystems and raising awareness among each and every employee through awareness-raising activities.
Since nature-related issues could impact our business, it is vital that we understand and manage how we are dependent on and how we impact nature throughout our entire value chain.
Objectives of Disclosure
Through proactive TNFD disclosure, the NGK Group will make clear the interface between our business and nature, ascertain the importance of our dependencies and impacts on nature, as well as related risks and opportunities, and meet the expectations of society and stakeholders. In addition, through disclosure the entire Group will promote nature-related initiatives, which will help to achieve the goal of coexistence with nature espoused in the NGK Group Environmental Vision and to bring about a sustainable society.
Overview of LEAP Approach
The TNFD recommendations endorse analysis based on the LEAP approach as a method for evaluating nature-related dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities. The LEAP approach consists of the processes: Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare, the details of which are shown in the table below.
Implementation Details of LEAP Approach
| Locate the Interface with Nature |
Evaluate Dependencies and Impacts |
Assess Risks and Opportunities |
Prepare to Respond & Report |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
TNFD Disclosure Recommendations and the Scope of Our Disclosure
Based on the TNFD disclosure recommendations, in FY2023, the NGK Group determined the interface between nature and our businesses and production sites. In FY2024, we assessed our dependencies and impacts at the production stage. We will now disclose the results of these exercises in accordance with the TNFD’s general requirements and the four pillars (governance, strategy, risk and impact management, and metrics and targets) and with reference to the LEAP approach.
TNFD Disclosure Recommendations and the Scope of Our Disclosure○: Meet disclosure recommendations △:Partially meet disclosure recommendations
| TNFD disclosure recommendations | LEAP approach referenced | Current disclosure scope | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governance | A. Board of Directors oversight | P | ○ | |||
| B. Role of executives | P | ○ | ||||
| C. Human rights policy with respect to stakeholders, engagement activity | P | ○ | ||||
| Risk and impact management | A(i). Processes to identify, assess and prioritize dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities in our own business | E | A | ○ | ||
| A(ii). Processes to identify, assess and prioritize dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities in our value chain | E | A | ○ | |||
| B. Processes for managing dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities | E | A | ○ | |||
| C. Integration with our organization’s risk management | A | ○ | ||||
| Strategy | A. Identify dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities | E | A | △* |
||
| B. Impacts of dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities on our business model, strategy and financial planning | P | △ | ||||
| C. Resilience of our strategy in different scenarios | A | P | ||||
| D. Locations of assets and/or activities that meet criteria for priority locations | L | E | A | △* |
||
| Metrics and targets | A. Metrics for measuring risks and opportunities | A | ||||
| B. Metrics for measuring dependencies and impacts | E | A | ○ | |||
| C. Targets and performance | P | ○ | ||||
Only production sites in our primary value chain included in the Results of Assessment of Dependencies and Impacts on Nature in Primary Value Chain table
General Requirements
The TNFD recommendations include six general requirements applicable to all four disclosure pillars. The NGK Group’s approach to these general requirements is as follows.
| General requirement | NGK Group approach |
|---|---|
| Application of materiality | Based on the concept of double materiality, the NGK Group works to address environmental and social issues by making efficient and effective use of our limited management resources, and aims to maximize value creation for both the Group and our stakeholders. We use the double materiality approach in our TNFD-based assessment and disclosure. |
| Scope of disclosures | We analyze and disclose relationships with nature (dependencies and impacts, risks and opportunities) for the whole NGK Group business. We have carried out a detailed analysis of the Group’s production sites taking account of the unique features of their locations. We have currently identified the broader picture for the rest of the value chain. |
| Location of nature-related issues | We have assessed whether the NGK Group’s main production sites meet the TNFD criteria for a sensitive location based on the unique features of their locations and designated those that do as priority locations. We are prioritizing action for sites with dependencies and impacts for critical natural systems. We have conducted a detailed analysis for NGK CERAMICS MEXICO because we think water risk merits prioritization. |
| Integration with other sustainability-related disclosures | The NGK Group regards ESG management as crucial to our vision for 2050. To this end, key nature-related issues we must address are responding to climate change, promoting resource recycling, preventing environmental pollution, and conserving and restoring biodiversity. The Group has fully implemented TCFD recommendations-based disclosure and this disclosure references some of its results. There is some overlap between TCFD-based and TNFD-based disclosure. We will consider how to align these to provide integrated disclosure. |
| Time horizons considered | The time horizons in our TNFD disclosure are: near-term: next 2-3 years; mid-term: through 2030; long-term: through 2050. |
| Engagement with indigenous peoples, local communities and affected stakeholders | Our NGK Group Human Rights Policy applies to all NGK Group executives and employees and we also require our suppliers to abide by this policy. The NGK Group Code of Conduct and NGK Group Supplier Code of Conduct define our human rights-related obligations in order to avoid violating the rights of indigenous peoples, local communities and affected stakeholders. We recognize the importance of engaging with stakeholders in our human rights due diligence and in the formulation and implementation of remedial measures. |
Governance
Board of Directors Supervision, Role of Executives
The NGK Group Environmental Vision, approved by the Board of Directors, calls for carbon neutrality, a recycling-oriented society and harmony with nature, and identifies the conservation and restoration of biodiversity as a Group materiality. The Sustainability Management Committee, chaired by the Representative Director and President and staffed by the committee chairs and Business Group Executives, formulates five-year environmental action plans and oversees progress towards management indicators and targets set each fiscal year. It also promotes activity throughout the value chain. The Committee reviews TNFD recommendations-based information disclosure and reports its findings to the Board of Directors. The Committee reports to the Board on this and its other activities at least once a year.
Sustainability Promotion Framework
Human Rights Policy with Respect to Stakeholders, and Engagement Activity
Respect for human rights within the NGK Group’s corporate activity is mandated by the NGK Group Corporate Business Principles, the NGK Group Code of Conduct and the NGK Group Supplier Code of Conduct. We are also guided by our specific NGK Group Human Rights Policy. In accordance with this policy, we have instituted a human rights due diligence process and are implementing measures to identify, prevent and mitigate adverse impacts on human rights in our business activities. When adverse impacts have been found, or are suspected, to have occurred, we are committed to engage in sincere dialog with the involved parties and to the implementation of appropriate and effective remedial measures. The Directors responsible for the Human Resources Department and the Sustainability Management Department, the General Managers of the Human Resources Department and the Sustainability Management Department, and the heads of business departments are responsible for implementing human rights measures in coordination and cooperation with related committees and departments, depending on the content and importance of individual measures. The Director responsible for the Human Resources Department regularly reports implementation progress to the Board for its oversight.
Risk and Impact Management
Process for Identifying, Assessing and Prioritizing Dependencies and Impacts, and Risks and Opportunities
Below, we outline the process for identifying, assessing and prioritizing nature-related dependencies and impacts, and risks and opportunities in the NGK Group business value chain. We provide further detail about the processes listed below in the Strategy section of this disclosure.
| Process | Content |
|---|---|
| Overviewing and identifying dependencies and impacts |
|
| Identifying critical nature-related risks and opportunities |
|
Processes for Managing Dependencies and Impacts, and Risks and Opportunities and Their Integration with Corporate Risk Management
The Sustainability Management Committee manages nature-related dependencies and impacts, and risks and opportunities in the NGK Group. It aligns the management of risks, in particular, with the risk management systems and processes determined by the Risk Management Committee for groupwide risk management.
Strategy
This section provides a more detailed explanation of the processes for identifying, assessing and prioritizing the dependencies and impacts, and risks and opportunities outlined in the Risk and Impact Management section.
Overviewing and Identifying Dependencies and Impacts
Overviewing Dependencies and Impacts in our Business Value Chain
We used evaluation tool ENPRIMARY*2 to ascertain the dependencies and impacts on nature in the industries in which we engage. In analyzing the dependencies on nature that we deem crucial to our business, we extended the use of this tool to the supply of non-living resources. This enabled us to organize the dependencies and impacts for our primary business value chain (procurement, production, logistic) into different levels.
2: ENPRIMARY is a tool that helps financial institutions, business enterprises and other organizations to understand the significance of individual industries’ dependencies and impacts on nature. It was developed by NGO Global Canopy, UNEP FI (United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative) and UNEP-WCMC (UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre).
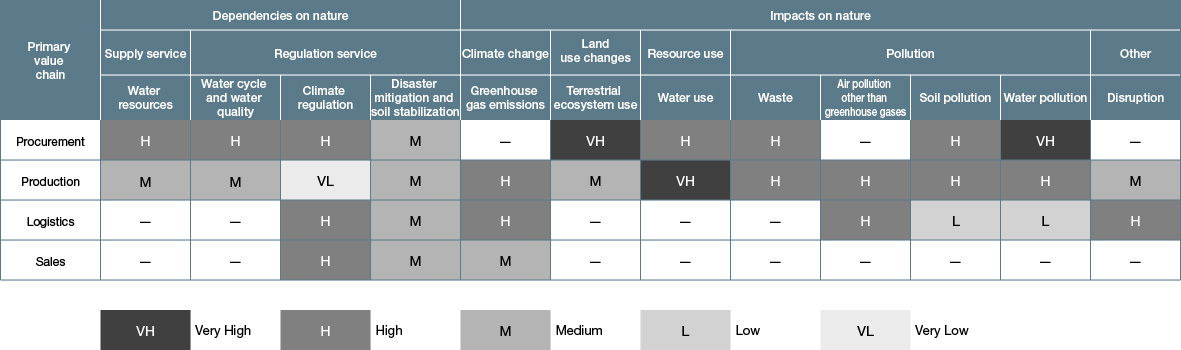
Results of Assessment of Dependencies and Impacts on Nature in Primary Value Chain
(assessment of industrial fields similar to that of the NGK Group)
Dependencies on Nature
Negative Impacts on Nature
Our key findings from this analysis are as follows.
Procurement:
Our major dependencies on nature in the metal mining and smelting, and nonmetallic minerals extraction processes are on supply services for water resources and non-living resources and on maintenance and restoration services, such as water purification and rainfall pattern adjustment. Our major adverse impacts on nature are our potential to cause effects on freshwater and marine ecosystems through their use and resource use, and to cause pollution through the discharge of soil or water contaminants and through disruption.
Production:
We have a slight dependency on supply services for water resources and non-living resources. Our major adverse impacts are our potential contributions to greenhouse gas emissions, causing climate change, and to pollution through the discharge of soil and water contaminants.
Logistics:
We are dependent on supply services for fuel and other non-living resources in the transportation of products and raw materials, and also on maintenance and restoration services, including transportation infrastructure provision, and flood control and storm mitigation services that mitigate disaster risk. Our major adverse impacts on nature are the potential for pollution caused by disruption and for the introduction of invasive non-native species.
Based on this understanding, we have specified the major dependencies and impacts of our production activities in the current disclosure.
Identifying Our Major Dependencies and Impacts
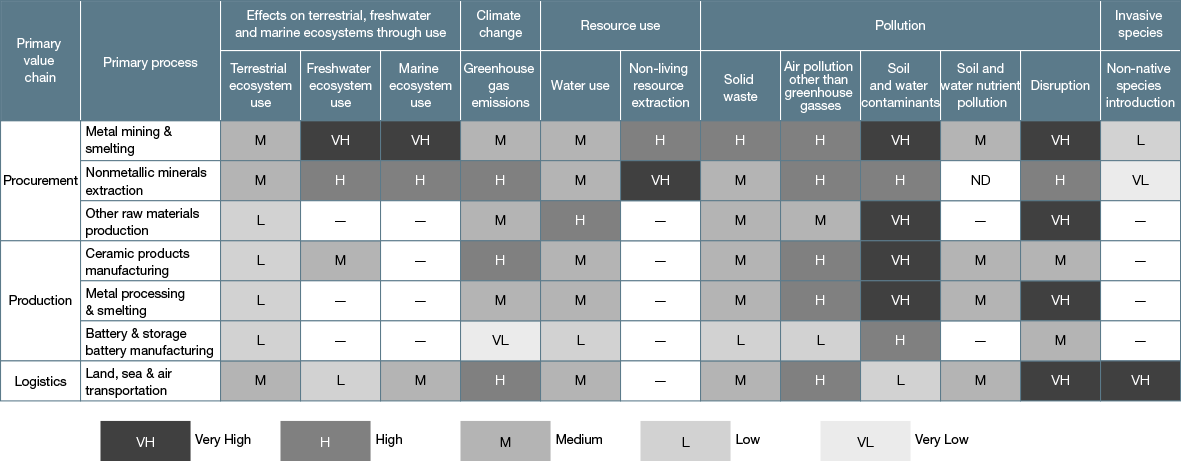
We undertook further analysis of the production dependencies and impacts rated VH, H or M in the production stage in the primary value chain to identify which are most significant in light of the NGK Group’s business activities. We did this with reference to data from a range of reference literature(1), production site environmental data and countermeasures implemented by each business. Through this process we determined that those issues that appear less relevant given the nature of our business, or whose potential to materialize appears sufficiently ameliorated by existing countermeasures, are less significant.
The figure below shows the relationships between the major dependencies, major impacts, related natural components (termed “environmental assets” by the TNFD) and impacts on these from outside the NGK Group for each business area.
(1) Reference literature
CDP Water Impact Index
World Bank Group, International Finance Corporation (IFC), Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Guidelines
European Commission, Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation - preliminary study on new product priorities
European Ceramic Industry Association (Cerame-Unie), Ceramic Roadmap to 2050
Major Dependencies and Actual and Potential Impacts on Nature, Related Natural and Environmental Assets and External Factors for the NGK Group’s Production Operations
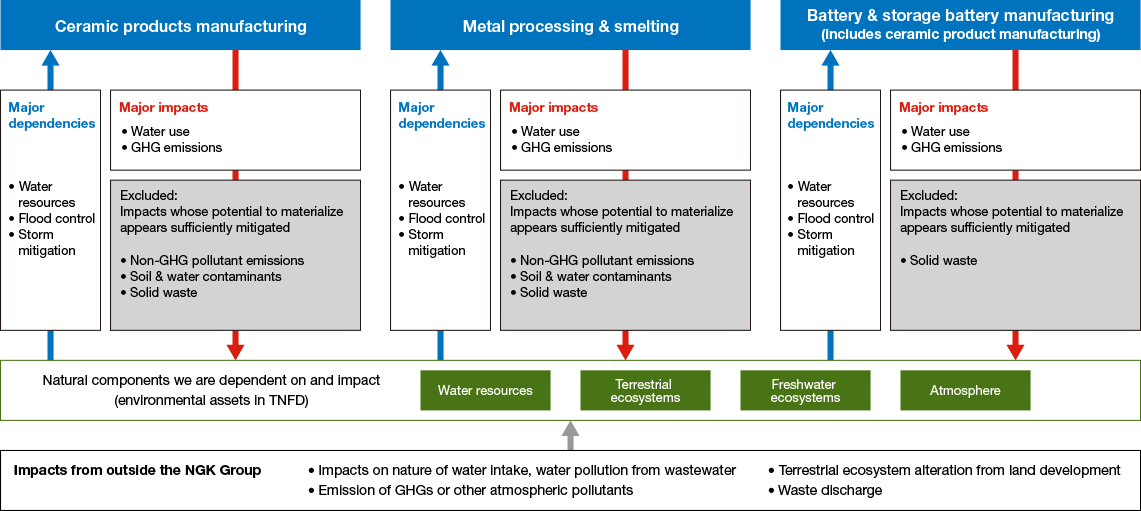
The following major dependencies and major impacts at the production stage in the NGK Group value chain emerged as a result of this process.
Major dependencies
・Water resources
・Flood control and storm mitigation services
Major impacts
・Water use
・Greenhouse gas emissions
Assessment and Selection of Activity Locations that Meet the Criteria for a Priority Location
The TNFD recommendations categorize “sensitive locations” and “material locations” as “priority locations.” Sensitive locations are locations that are ecologically vulnerable to impact regardless of specific business dependencies or impacts. These include the habitats of rare or endemic species, pristine environments and areas with high water stress.
Material locations are locations where an organization has major dependencies and/or impacts on nature and has a particularly strong relationship with the natural environment.
We determined our priority locations by assessing whether each of the NGK Group’s 39 production sites in and outside Japan constitute a sensitive or a material location. We are prioritizing addressing issues at production sites in priority locations.
Sensitive Location Assessment
The TNFD recommendations cite areas “important for biodiversity” and/or “of high ecosystem integrity,” and/or “of rapid decline in ecosystem integrity,” and/or “of high physical water risks” as the criteria for sensitive locations. We used metrics relating to each of these criteria in assessing the status of our production sites.
| Sensitive Location Criteria | Related Metric |
|---|---|
| Important for biodiversity/high ecosystem integrity*6 |
|
| Rapid decline in ecosystem integrity |
|
| High physical water risks |
|
3: Areas designated as protected areas by local or national governments or by international treaty
4: A KBA (Key Biodiversity Area) is an area important to the preservation of biodiversity selected using generally accepted scientific criteria and standards
5: Conservation priority is the indexed measure of the level of risk of species loss when an area undergoes development
6: Ecosystem integrity is a metric for ecosystem health; urbanized areas have low ecosystem integrity
7: The Biodiversity Intactness Index (BII) estimates how much of an ecosystem’s natural biodiversity still remains despite human impacts
8: The human footprint is the total environmental impact of all human activities (urban development, agricultural development, transportation, etc.)
(2): Calculated based on the number of species and endangered species, and the size of each species’ habitat, in an area using big data about species distribution from Think Nature Co., Ltd.
(3): Calculated by Think Nature Co., Ltd. using the IUCN’s habitat map (showing the degree of nature loss due to land usage and change) and the distribution of natural forests
(4): Mu, H., Li, X., Wen, Y., Huang, J., Du, P., Su, W., ... & Gang, M. (2022). A global record of annual terrestrial Human Footprint dataset from 2000 to 2018. Scientific Data, 9(1), 176
(5): Aqueduct Baseline Water Stress indicator, World Resources Institute (WRI)
(6): Surface Water Quality Index component of the WWF Water Risk Filter
(7): Hazard map used during TCFD risks and opportunities assessment
■ Important for Biodiversity/High Ecosystem Integrity
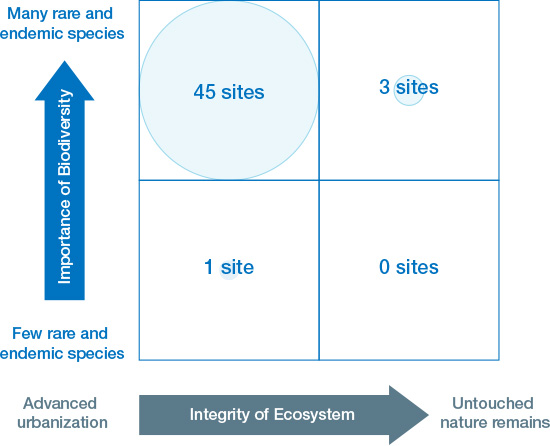
Locations that are important for biodiversity are those that are valuable to biodiversity primarily because they contain a large number of rare or endemic species and constitute a healthy ecosystem. Locations with high ecosystem integrity are those that have experienced little man-made change and hence continue to constitute a healthy natural environment. We used the conservation priority index, based on the number of rare or endemic species, to assess importance for biodiversity, and the Biodiversity Intactness Index (BII) to asses ecosystem integrity. As a result, we categorized 38 production sites in areas with high conservation priority as sensitive locations important for biodiversity. These sensitive locations include six sites in Japan or Europe that are within 500 meters of a protected area (IUCN Category IV*9: habitat or species management area) or an area important for biodiversity, and three in countries such as Mexico that are in regions with high ecosystem integrity.
These are areas in which our business activities could have a negative impact on the natural environment that threatens biodiversity or ecosystem health. However, we believe that the environmental measures the NGK Group is already taking in our business activities to counter the possibility of biodiversity impact from activity such as pollutant emission limit the adverse impact of our sensitive location sites on the surrounding natural environment.
9: IUCN Category IV: designation for the protection or restoration of globally, nationally or regionally important flora, fauna or habitats
■ Rapid Decline in Ecosystem Integrity
Areas experiencing rapid decline in ecosystem integrity are those whose natural environment has been degraded to the point that it is highly vulnerable and has little resilience to external pressures. Given the inexorable rise in human footprint indicators, which measure the impact of human activity on the natural environment, we believe that there has been great change in the natural environment and that ecosystem integrity is declining. After ascertaining change in the human footprint in areas around our production sites, we categorized 12 of them as sensitive locations with declining ecosystem integrity, most of which are in Asia, Europe and North America.
■ High Physical Water Risks
We assessed our water risks using three metrics: water stress, water pollution and flood risk.
- Areas with high water stress are those in which water demand exceeds water supply in the drainage basin. Insufficient water to meet an ecosystem’s needs could result in severe change in the natural environment due to the drying up of rivers or wetlands or other deteriorations in natural organism habitats. After assessing water stress using the Aqueduct Baseline Water Stress indicator, we categorized 12 of our production sites as sensitive locations with high water stress, most of which are in Asia, Europe and North America.
- Deterioration in water quality could threaten ecosystems or human living conditions in areas with water pollution. We used the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) component of the Surface Water Quality Index to assess surface water pollution, and assessed electrical conductivity and the level of nutrients such as nitrogen. As a result, we categorized 26 of our production sites in mainly urban areas of Asia, Europe and North America as sensitive locations with water pollution. The NGK Group not only complies with all regional laws and regulations relating to the prevention of water pollution but we have also instituted our own even higher standards. Consequently, we believe that we cause little adverse impact in terms of water pollution.
- Areas with high flood risk are those at high risk of river overflow or high tides, which could cause soil runoff, deterioration in water quality or the destruction of natural habitats. After checking against the hazard map we used when we did our TCFD risks and opportunities assessment, with flood risk one of the physical risks due to climate change, we categorized eight of our production sites in Japan or the rest of Asia as sensitive locations with high flood risk.
Material Location Assessment
The TNFD recommendations define a material location as one in which an organization has major dependencies and impacts on nature in its business activities. The identification of our major dependencies and impacts determined that the NGK Group’s major dependencies at the production stage are water resources, and flood control and storm mitigation services, while our major impacts are water use and greenhouse gas emissions.
We recognize that our dependency on water resources and the impact of our water use are high in areas with high water stress. We, therefore, categorized our 12 production sites in areas with high water stress as material locations for dependency on water resources and water use impact.
We regard our dependency on flood control and storm mitigation services as high in areas experiencing a decline in ecosystem integrity and/or with high flood risk. We, therefore, categorized our 19 production sites in such areas as material locations for dependency on flood control and storm mitigation services.
We regard the impact of our greenhouse gas emissions as a vital issue for all our production sites, wherever they are located. We have already been assessing and addressing this under our TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) disclosure and have, therefore, omitted this from this TNFD disclosure.
Priority Location Assessment
We combined our sensitive locations and material locations assessments to determine our priority locations. This resulted in the identification of 22 production sites, mainly in Mexico, Belgium, China and Japan, where we need to address issues on a priority basis. We will now conduct an appropriately detailed investigation of these sites. We will discuss our water stress assessment at NGK CERAMICS MEXICO at the end of this disclosure as an early example of such an investigation.
Positive Impacts from Our Goods and Services
So far, our primary focus has been on the negative impacts on nature from the NGK Group’s businesses and the nature of our production site locations. However, we believe that the Group’s business also makes a positive contribution to nature. The table below summarizes the positive impacts of the NGK Group’s primary products and services on nature, with reference to the causes of natural change in the TNFD recommendations.
| Business content | Main products & services | Change in land use | Climate change | Resource use | Pollution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial ecosystem use | GHG gas emissions | Non-living resource extraction | Solid waste | Non-GHG atmospheric pollution | Soil pollution | Water pollution | |||
| Environment Business Group | Automotive Ceramics Business | Ceramics for purifying auto exhaust | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| NOx sensors | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Industrial Process Business | Industrial heating systems, refractory products | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Membrane separating systems | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| High-temperature dust collectors | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Low-level radioactive waste treatment units | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Digital Society Business Group | High Performance Ceramics Business | Ceramics for semiconductor manufacturing equipment | ● | ||||||
| Electronic Devices Business | EnerCera | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Power Electronics Ceramics Business | AMB substrates | ● | ● | ||||||
| Specialty Metals & Molds Business | Special metals and mold products | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Energy & Industry Business Group | Energy Storage Business | NAS batteries | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Insulator Business | Insulators | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
Ceramic products are generally characterized by high heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and durability, which contribute to their long service life. Compared to other materials, they help reduce the consumption of raw materials and the generation of waste. Taking advantage of these characteristics, we expect that our Group’s major products and services can contribute to mitigating our negative impact on nature.
For example, our ceramics for purifying automobile exhaust feature an ultra-thin wall structure that provides high performance. Compared to conventional products, our products are able to purify harmful substances contained in automobile exhaust gases more effectively.
Products and Services Contributing to Environmental Protection
Identifying Our Major Nature-related Risks and Opportunities
Below, we summarize the risks and opportunities we currently envisage, with reference to the categorization of risks and opportunities in the TNFD recommendations.
For risks, we started by establishing assumptions for their likelihood and potential severity and then made a qualitative assessment of their priority order. We drew up a list of risks we deem most significant and the countermeasures we envisage based on the results of this process.
For opportunities, given the difficulty of anticipating what possibilities may arise, we drew up a list of opportunities we currently envisage based on inputs such as the positive impacts of our products and services. Since we have already delineated the risks and opportunities relating to greenhouse gas emissions under our TCFD disclosure, we have omitted this from this TNFD disclosure.
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
Major Nature-related Risks
| Risks | Dependencies/impacts | Risk | Timeframe | Countermeasure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition | Govt. policy | Impact Water use in production process |
|
Mid-term~ |
|
| Impact Impacts on terrestrial/freshwater/marine ecosystems from mineral extraction/mining operations |
|
Mid-term~ |
|
||
| Market | Impact Raw materials production |
|
Near-term~ |
|
|
| Technology | Impact Resource use in production process |
|
Near-term~ |
|
|
| Reputation, liability | Impact Atmospheric pollutant emission during production process |
|
Near-term~ |
|
|
| Impact Water pollutant emission during production process |
|
Near-term~ |
|
||
| Physical | Acute | Dependency Water resource supply, flow adjustment in our production process |
|
Near-term~ |
|
| Dependency Flood control/storm mitigation in our production process |
|
Near-term~ |
|
||
| Dependency Flood control/storm mitigation, rainfall pattern adjustment in upstream supply chain |
|
Near-term~ |
|
||
| Chronic | Dependency Water resource supply, flow adjustment in our production process |
|
Mid-term~ |
|
|
| Dependency Water resource supply, flow adjustment in upstream supply chain |
|
Near-term~ |
|
||
Major Nature-related Opportunities
| Category | Positive impact | Opportunity | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market/products & services |
|
|
Mid-term~ |
|
|
Mid-term~ | |
|
|
Mid-term~ | |
| Resource efficiency/reputation |
|
|
Mid-term~ |
| Reputation |
|
|
Mid-term~ |
|
|
Mid-term~ |
Metrics and Targets
The TNFD recommendations call on organizations to disclose the metrics and targets they use to assess and manage their nature-related dependencies and impacts, and risks and opportunities. Regarding metrics, the NGK Group analyzes and discloses a range of environmental data relating to our business activity. Regarding targets and performance, we are progressing our fifth 5-Year Environmental Action Plan to manage environmental targets in the period FY2021-25.
The table below is an up-to-date summary of the metrics we are using in alignment with The TNFD’s core global metrics.
| Metric no. | Driver of natural change | Indicator | Metric (as of Aug, 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | Climate change | GHG emissions | See Environmental Data Collection, GHG Emissions |
| C1.0 | Land/freshwater/ ocean-use change |
Total spatial footprint | Total surface area controlled/ managed by the organisation, where the organisation has control (km2): 4.1 km2 (total site area managed by NGK Group) |
| C1.1 | Extent of land/freshwater/ ocean-use change |
Area of land we are autonomously conserving: 0.1 km2 (area of NGK Minnano Mori Mizunami forest, designated a Nationally Certified Sustainably Managed Natural Site by the Ministry of the Environment) |
|
| C2.0 | Pollution/pollution removal | Pollutants released to soil split by type | No soil contamination |
| C2.1 | Wastewater discharged | See Environmental Data Collection, Conservation of Water Resources | |
| C2.2 | Waste generation and disposal | See Environmental Data Collection, Discarded Materials | |
| C2.3 | Plastic pollution | See Environmental Data Collection, Discarded Materials (plastic recycled + disposed of externally) | |
| C2.4 | Non-GHG air pollutants |
See Environmental Data Collection, Chemical Management System (VOC, PRTR-listed substances (emissions into atmosphere) |
Carbon Neutrality Strategic Roadmap and 5-Year Environmental Action Plan
Future Initiatives
As called for by the TNFD disclosure recommendations and noted earlier in this disclosure, we plan to conduct a detailed assessment of our dependence and impact on nature along the upstream of our value chain, including the extraction and mining of raw materials. We also plan to examine nature-related risks and opportunities using scenario analysis. For measurement metrics and targets, we will continue referring to global core disclosure metrics outlined in the TNFD recommendations while also expanding our evaluation of data collection and targets. At the same time, we will enhance our disclosure content as we aim to achieve disclosure for all items based on the TNFD recommendations.
Reference
Priority Location In-depth Assessment: Water Stress Assessment for NGK CERAMICS MEXICO
NGK CERAMICS MEXICO serves as a good example of an in-depth assessment of a production site we have identified as a priority location. It is located in an area with a high level of water stress and mainly uses groundwater. It is generally harder to ascertain information pertaining to the water source, such as water level fluctuation, for groundwater than for surface water. However, we used Geosphere Environmental Technology Corp.’s GETFLOWS water cycle simulation model to facilitate an assessment of conditions in the local drainage basin and impacts on the surrounding area from the production site’s water use. We outline our in-depth assessment process in the table below. This includes our assessment of the impact of the site’s water intake and of the level of water stress.
Assessment Process
| Assessment process | Main actions |
|---|---|
| Build a water cycle model | Construct a water cycle simulation model using climate, terrain, land use and land cover, geological and water use data inputs |
| Identify drainage basin | Use the simulation to identify the catchment area for the groundwater intake and the area this impacts |
| Assess water intake impact | Assess the extent and amount of impact the groundwater intake has on the surrounding area |
| Assess water stress | Assess the level of stress on the water catchment area and drainage basin |
Water Intake Impact Assessment for NGK CERAMICS MEXICO
To understand the impact NGK CERAMICS MEXICO’s water intake has on the groundwater level in the surrounding area, we used the simulation to estimate the difference in groundwater level for two scenarios: the first with and the second without groundwater intake by the production site. This revealed a decline in the groundwater level of around 0.15 meters in the area immediately surrounding NGK CERAMICS MEXICO (location marked with a star on the map below) and a decline of around 0.1 meters in the area within a roughly one-kilometer radius of the plant. By comparison, groundwater level monitoring in the region shows a seasonal fluctuation of 2–6 meters. These results indicate that NGK CERAMICS MEXICO’s water intake reduces the groundwater level by only a limited amount.
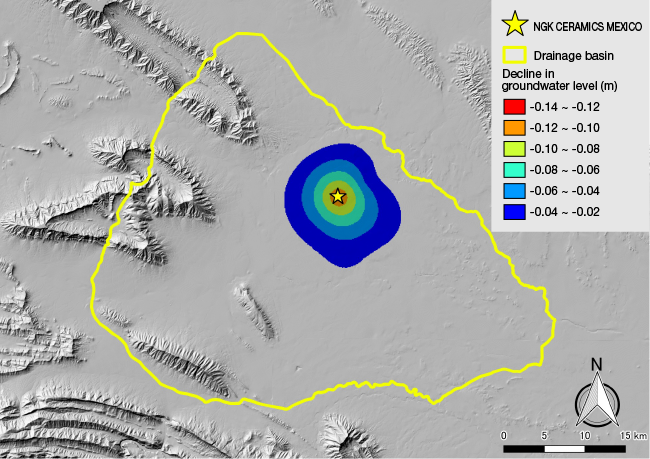
In-depth Water Stress Assessment for NGK CERAMICS MEXICO
The water intake impact assessment described above revealed that NGK CERAMICS MEXICO’s water intake has only a limited impact on groundwater levels.
However, we carried out an in-depth assessment of the level of water stress to understand the necessity of water resource management to support the longer-term continuation of our business activities in this area. Our analysis also made use of literature about the levels of water demand and water resources in the area, both for the entire drainage basin and the plant’s water catchment area. This assessment looked not at NGK CERAMICS MEXICO’s actual water intake but at water resource conditions for the entire region in which the production site is located.
To ascertain the level of water stress in NGK CERAMICS MEXICO’s water catchment area (the area inside the dotted line on the map below) and the entire drainage basin (the area inside the yellow line), we carried out a three-dimensional simulation of the groundwater and surface water flow paths. This revealed that the water taken in by the production site is water that permeates eastwards from the elevated area to its west, indicated by the blue arrows on the area inside the dotted line. Our assessment of water stress indicated that the severity of water stress is at the third level on a five-point scale (low; low-medium; medium-high; high; extremely high)*10 for the plant’s water catchment area and at the fourth for the wider drainage basin that includes the production site and areas further downstream.
10: Water stress severity: Five-point scale in the World Resources Institute’s Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas
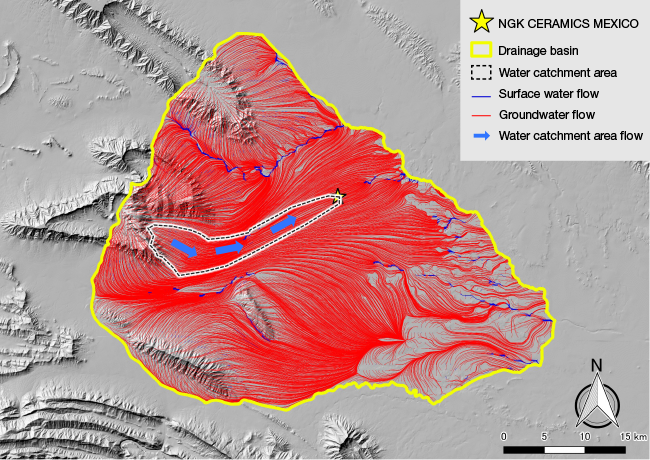
The NGK Group has been assessing water risk at our main production sites since before we carried out this simulation. Consequently, we already understood that NGK CERAMICS MEXICO is in an area of high water stress and had already implemented countermeasures, such as water reuse, at the plant. However, in alignment with the recent trend for water resource management to become common practice, we will use the results of this assessment together with the plant’s actual water intake data to inform the continued implementation of measures to reduce water stress in the plant’s water catchment area and the wider drainage basin.
