Sustainability
Risk Management
Basic Approach
The NGK Group considers uncertainties which may affect achievement of the Group Vision to be risks. We have established an approach of handling risks according to their type, which enables us to control these risks by appropriately recognizing and preventing them, and to minimize losses caused by risks that do materialize.
Moreover, when risks that have a big impact on management occur, the committee tasked with handling the risk according to the Basic Rules of Crisis Management will lead the way in collecting information and ascertaining the situation. The NGK Group will then work to minimize the negative impacts, analyze the causes, and prevent recurrence. For extremely serious risks, the executive officer in charge of the Sustainability Management Dept. will convene a response meeting attended by the President to respond to the risk.
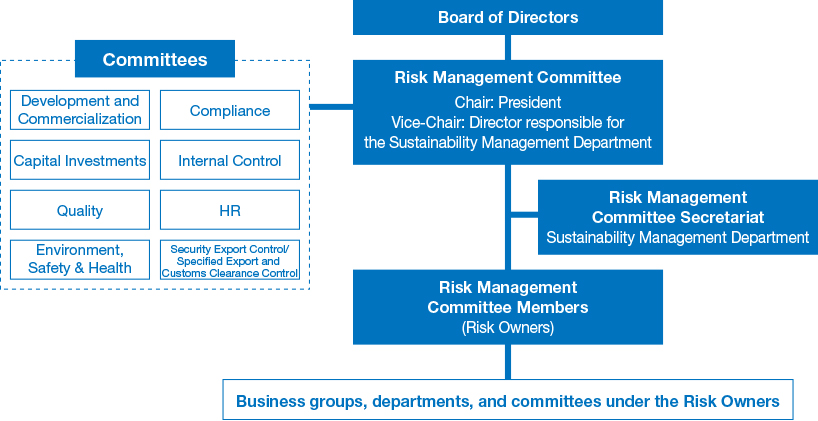
Risk Management Structure
In FY2023, the NGK Group established a new Risk Management Committee chaired by the President, and is comprehensively managing the Group's significant risk issues under the supervision of the Board of Directors in accordance with the risk management process described below. Risk Management Committee members perform management activities which include providing direction and support to each division and department for handling risks in the area they are responsible for. In addition to crafting and carrying out risk countermeasures, each business group and division also constantly monitors the materialization of risks and reports these results to the Risk Management Committee. At least once a year, the Risk Management Committee reports to the Board of Directors about risk management activities. Through this, the Board of Directors is able to supervise these efforts and verify the effectiveness of the risk management structure. The risk management structure in question, is managed independently of the Audit & Supervisory Board.
Risk Management Structure
Risk Management Process
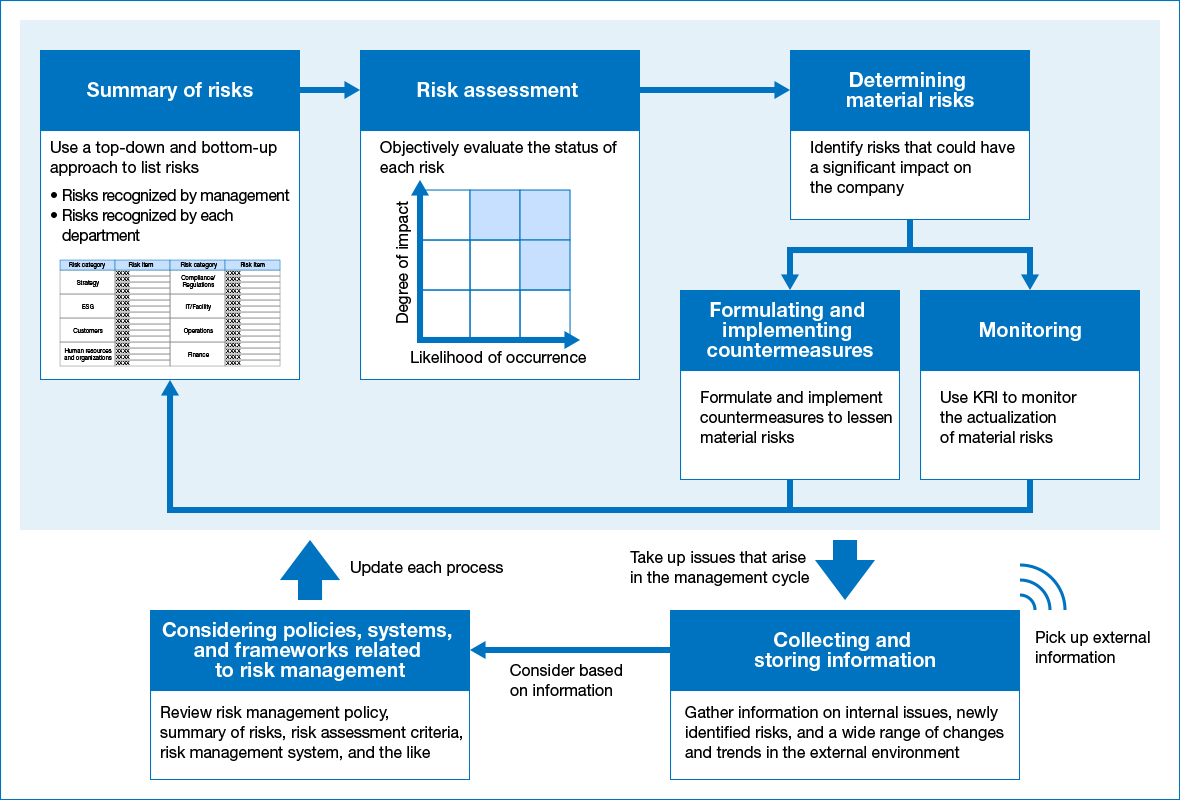
The Board of Directors views uncertainty that affects the achievement of the NGK Group Vision as risk, and has decided on a concept of risk management to serve as our policy concerning risk management. It determines the approach to take on initiatives depending on the classification of risks as “risks NGK should take” or “risks NGK should avoid.” Under this approach, the Risk Management Committee periodically analyzes and evaluates risks, then identifies and reviews the material risks that should be managed based on changes in the internal and external environment, with reference to the COSO-ERM Framework*. It has also established a risk management structure and method for formulating and implementing countermeasures against risk and monitoring the manifestation of risks via the committees and departments in charge of managing risks. Once a year, we identify the risk factors impacting our business operations in both a top-down manner by management, and a bottom-up manner by each department, in order to identify and review critical risks. We check the level of impact of each risk, changes in the likelihood of their occurrence, and whether we are aware of new risks, then review our risk assessment. Through these efforts, the Risk Management Committee manages the risks facing the NGK Group in an interdisciplinary manner, and reports to the Board of Directors.
In order to flexibly address risks that have suddenly increased in importance due to abrupt changes in the internal and external environment, we make sure we are able to respond by adding them in a timely manner to the list of targets to be handled by the Risk Management Committee. Following the change of administration in the United States in FY2024, we held discussions focused on tariff policy and its impact on our business with outside experts at Risk Management Committee meetings.
COSO-ERM: An international framework created by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in the USA, that aims to manage the risks facing businesses and integrate strategy and performance.
Material Risk Management Cycle
Risks, Summary, Response
| 1. Business operation risks | All operations |
|---|---|
|
Risk summary
|
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Environment Business | |
|
Risk summary
|
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Digital Society Business | |
|
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Energy & Industry Business | |
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 2. R&D-related risks | Risk summary
New Value 1000: A target of reaching 100 billion yen in sales from new products and new businesses by 2030 |
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 3. Personnel Risks | Securing and managing personnel |
|
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Support diversity and inclusion | |
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 4. Legal compliance, human rights and safety, and quality-related risks | Legal compliance-related risks |
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Human rights and safety-related risks | |
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Quality and product safety-related risks | |
Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 5. Information systems-related risks |
Risk summary
|
Response
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 6. Currency exchange, capital, and procurement-related risks | Risk summary
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| 7. Climate change and disaster-related risks | Climate change-related risks |
|
Risk summary
|
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Residual risk
|
|
| Large-scale disaster and infectious disease-related risks | |
|
Risk summary
|
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Residual risk
|
Legal Risk Management in Overseas Subsidiaries
The NGK Group is working on understanding better legal risk management by overseas subsidiaries to minimize risks which become global and varied due to overseas business expansion.
We ask all overseas subsidiaries to report information pertaining to the status of lawsuits, legal affairs and consultation with lawyers twice a year, and whistleblowing system usage, export controls and access to legal-related information once a year. Major issues mentioned in such reports are reported to and shared at the Compliance Committee. Consultations from overseas subsidiaries are handled by the legal department and by lawyers, if necessary, to avoid risks.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Initiatives
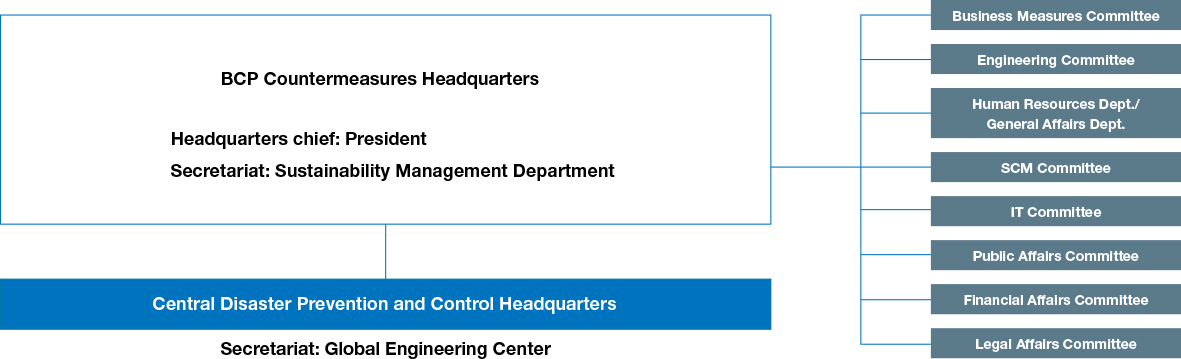
At NGK, we have established the BCP Countermeasures Headquarters under the direction of the President as an organization to carry out operation and maintenance of our business continuity plan, with the aim of respecting human life and cooperating with the local community. It promotes our business continuity plan (BCP) throughout the entire NGK Group. Measures taken in preparation for putting our BCP into operation include the establishment of multiple manufacturing bases and procurement sources, damage mitigation measures related to buildings and equipment, and employee safety assurance. We also conduct emergency drills based on scenario plans presuming a major disaster such as a large earthquake in the Nankai Trough with the aim of enhancing our ability to cope with a crisis in the event a disaster occurs. During these drills, participants are instructed to take real action according to the plan. This helps us to identify even small issues with each process and procedure and use our findings to improve the BCP. In addition, the BCP Secretariat leads the way in working to ensure business continuity by collecting information early on and implementing countermeasures in response to procurement difficulties stemming from the spread of infectious disease or changes in the global situation.
BCP Organizational Structure
FY2024 Initiatives
Education |
|
|---|---|
Awareness |
|
Training |
|
Other |
|
Future Initiatives
- Improve the effectiveness of BCP by raising the level of training further (e.g., hold BCP training for operational units)
- Ongoing support for home disaster prevention initiatives (dealing with those who are unable to return home after a disaster and providing drills for returning home in an emergency, etc.) from the perspective of respect for human life, which is the top priority of BCP
- Continue to hold education, training, and disaster preparedness events with the aim of improving the BCP/disaster prevention awareness of each and every employee
