Sustainability
Pursuing Quality for Products and Services
Basic Approach
Guided by the Corporate Philosophy, which puts customers first, the NGK Group considers the provision of products and services that contribute to a better social environment to be one of its most important missions in attempting to create quality from the customer’s perspective. We position the pursuit of safety in our products and services as one of our key material issues.
The NGK Group defines Quality Objectives each year in accordance with the Quality Policy based on the NGK Group Corporate Business Principles and Code of Conduct. This policy is focused on working to improve the quality of our operations* and reduce quality risks as our primary activities to increase customer trust. Moreover, we enhance our activities to increase customer trust by carrying them out in tandem with quality improvement activities.
Quality of operation: Quality of the operations that are in place to ensure that promises made to customers are fulfilled
NGK Group Corporate Business Principles and Code of Conduct
Quality Objectives FY2025
Everyone from management to frontline workers in the field thoroughly discusses overburden, waste, and unevenness in our operations, and works to improve them.
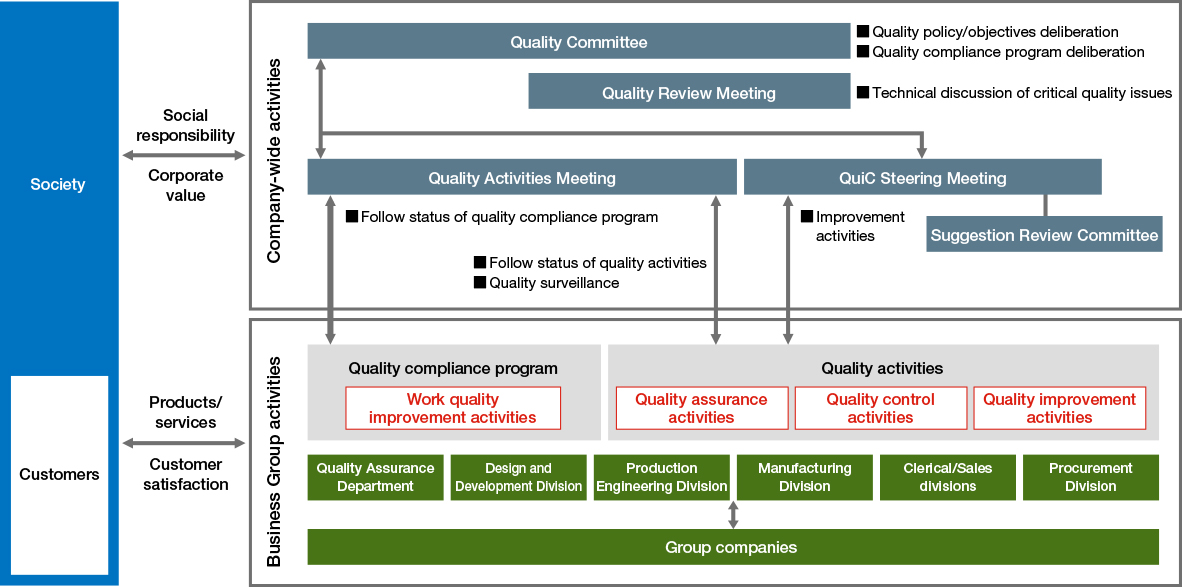
Quality Activity System
The NGK Group quality activity system consists of a company-wide system, led by the Quality Committee Chair (Director and Managing Executive Officer), and business division internal activity systems, led by the heads of each business group. In terms of company-wide activities, the Quality Committee was established to function as a deliberative body assisting the Quality Committee Chair, while business division internal activity systems were put in place for each business division, creating appropriate quality systems for each. Quality assurance, quality control, quality improvements, and quality education activities are promoted by the acquisition of ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification.
Each business group maintains a point of contact with customers, and works to further increase customer satisfaction by reflecting customer demands and things learned from quality problems in the market in our products and services.
Quality Activity System
Quality Control Systems Outside Japan
From their inception, production bases outside Japan have created quality systems appropriate to their situations and acquired ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification.
Monthly reports from each base regarding customer complaints and the status of manufacturing quality are discussed at Quality Activity Meetings, enabling the entire NGK Group to evaluate the quality status in a timely manner. Moreover, quality activity rules and annual quality objectives are distributed group-wide in an attempt to develop and enhance quality activities.
Acquisition of ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 Certification
All of NGK’s production sites, supporting functions and locations, and those of its Group companies in and outside Japan, have acquired ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification.
Activities to Increase Customer Trust
Improving Quality of Operations
We have continued to work on the initiative to improve quality of operation, which we started in FY2018, as our company-wide quality compliance program. These include declarations of intent from management, establishing rules and regulations, conducting training, audits and monitoring, and preventative activities. In FY2023, through our efforts to prevent overburden and ambiguity in operations, ensure thorough communication, and educate staff about our frontline workers reporting system, we reviewed workloads and work rules, and made progress on the understanding and dissemination of quality compliance in our workplaces and the frontline workers of operations at Group companies.
In FY2024 we further expanded our activities to include holding executive lectures for successorship, distributing educational videos for all people in management positions, and having members consider the risks of their own involvement. We have seen that everyone from directors and members of management to the frontline workers are increasingly taking ownership of quality compliance thanks to the activities we undertook up until FY2023, as well as the three activities we focused on in FY2024. In FY2025, we will encourage members to transfer this awareness into the ordinary course of business, and work to make our departments even more independent.
Reducing Quality Risks
4 Rules for Quality Activities
The NGK Group promotes restructuring of its quality activities to respond more precisely to increasing and diversifying quality demands from customers in different target markets. We have formulated these quality activity rules particularly to enhance the elimination of quality risks in the market, and are promoting their adoption and improved effectiveness.
Quality confirmation rule
Establish milestones, from development to start of production, and confirm conformance with six quality items when production processes change.
DR* function strengthening rule
Register DR plans with quality risks of medium or high level as important DR subjects with participation of company-wide DR reviewers. The General Manager of the Corporate Quality Management Dept. holds company-wide DRs for cases with a particularly high risk level.
Quality monitoring rule
Monitor and share information company-wide with respect to quality status changes or problems concerning manufacturing or markets. Manufacturing defects and customer complaints are shared company-wide every month through reports to the Corporate Quality Management Dept., and the appropriateness of countermeasures is discussed.
Rule for handling major customer complaints
In the event of a serious customer complaint, including a potential complaint, the situation is promptly reported to the Quality Committee Chair to formulate company-wide countermeasures.
DR: Design Review
QRE-P Activities
We have been promoting QRE-P activities* throughout the NGK Group since FY2017. Through these activities, we can identify business procedures that reveal the mindset and method for developing products and services in order to eliminate quality risks while improving quality. We have worked to incorporate the QRE-P concept into quality systems in each department, and have focused on providing practical training using development projects as examples.
In FY2024, together with departments we analyzed the business procedures that were causes of problems in the market, as we began doing in FY2023. Sharing points that can be improved has allowed departments to implement initiatives to improve their own systems and aim to more effectively and efficiently eliminate quality risks in development projects. At the same time, we continued to join the research and development departments in considering quality risks in accordance with QRE-P from an early stage in development before commercialization. In addition, we continued to roll out QRE-P activities not just to Group companies inside Japan, but outside Japan as well. As a result, staff understanding of the QRE-P concept is spreading.
In FY2025, we plan to narrow the targets of our business procedure analysis support and focus on these to make them more effective. At the same time, we will promote the further adoption of these concepts by continuing to roll out our QRE-P activities to development departments and Group companies. As a new initiative, we will take a customer perspective and begin focusing on the value of the experiences and inspiration that can be gained through the use of products and services, as opposed to the products and services themselves. As we do so, we will analyze the quality risks this entails as well. Moreover, we will continue our regular QRE-P activities for pursuing safety for products and services.
QRE-P (Quality Risk Elimination Process): An operational protocol intended to more effectively eliminate quality-related risks at every stage when bringing products to market, from product planning to mass production.
Pursuing Safety for Products and Services
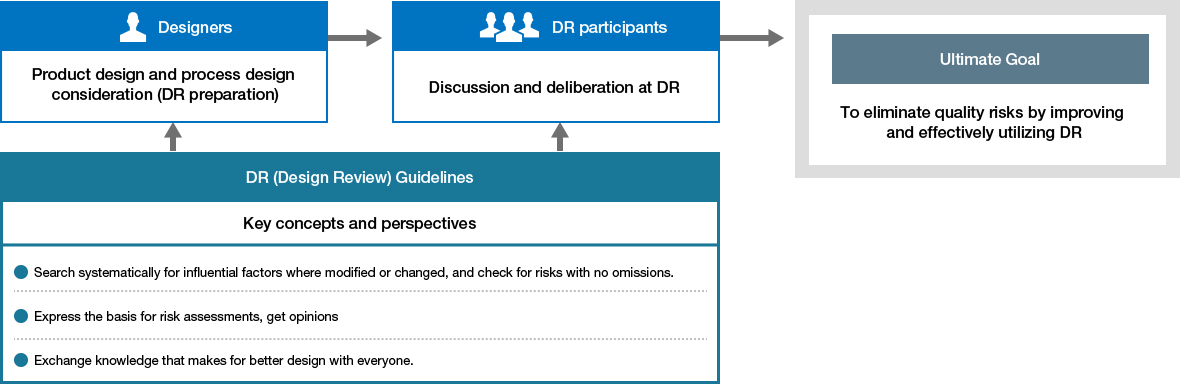
Activities to Strengthen DR Functions
The increasing and diversifying quality demands from customers call for the integration of knowledge among various members throughout the development process, not only from the design department but also from the manufacturing and production engineering departments. For this reason, the NGK Group considers DRs to be the most critical activity. DRs are conducted when development milestones are reached or when production processes change. Critical DRs are conducted by reviewers from throughout the company to support the elimination of quality risks.
The DR Guidelines were created to promote DR discussions and to thoroughly eliminate quality risks. We are constantly enhancing the effectiveness of DRs through efforts to spread these guidelines company-wide, including awareness and review of each DR.
Furthermore, NGK organizes a company-wide DR (quality review meeting) for quality issues that are difficult to solve by one department. At this meeting, relevant engineers and experts from across the company discuss broad aspects of issues related to the reliability and safety of products.
We are also deploying the above-mentioned QRE-P approach to facilitate improvement of design level at the pre-DR period as well as to ensure the more effective utilization of organizational knowledge and experience from DRs.
Flow of DR Activities
System for Considering ESG During Product Design
We design and develop products and services in accordance with the NGK Group Corporate Business Principles and Code of Conduct. As we strive to comply with the requirements of our customers and supply chain, we consider ESG by designing and developing quality management systems in accordance with the concept of QRE-P and the requirements of international standards (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.). Output which takes into account QRE-P concepts like QFD and FMEA is shared and deliberated through DRs and other examinations by those involved at the appropriate stage of development. In addition, we check implementation status through periodic internal audits of our quality management systems, and with audits conducted by our customers, supply chain, and certification authorities.
Quality Improvement Activities
QuiC Activities
Since FY2003, the NGK Group has held QuiC (Quality up innovation Challenge) quality improvement activities in which all employees participate. These activities consist of quality improvement activities by small groups or individuals and suggestions that strive to enhance the quality of products, services, and work; best practices are then shared by the entire NGK Group. Every July, NGK holds a company-wide contest at its headquarters to highlight examples of outstanding improvement activities with the intent of horizontal expansion throughout the company. Plus, since FY2021, we have revised our proposal evaluation methods to prioritize content in addition to quantity. In July of FY2024, we held the Company-wide QuiC Activities Contest. In October we held the NGK-BOX/Surprising Challenges! best practices presentation. The NGK-BOX/Surprising Challenges!, which we started in FY2021, provides a company-wide forum for laterally sharing reform examples and model initiatives in order to boost employee motivation and invigorate the workplace. So we held the event in FY2024 as well. Holding this event both online and in-person promoted communication between participants and helped to further increase motivation.
In FY2025, we will continue these activities, and pursue further quality promotion activities that all employees will take part in.
Suggestion Activity Participation Rate
| FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Department | 82% | 89% | 88% | 85% |
| Non-manufacturing Department | 71% | 76% | 69% | 45% |
| Clerical Department | 25% | 27% | 26% | 11% |
| Number of suggestions | Approx. 16,400 | Approx. 15,600 | Approx. 14,500 | Approx. 10,800 |
| Excellent Proposal Ratio | 18.2% | 20.7% | 24.5% | 30.7% |



NGK-BOX/Surprising Challenges! best practices presentation
External Improvement Case Study Symposiums
We shared examples of quality improvement activities we have engaged in at four conventions outside the company: The QC Circle Case Study Symposium and the Business Improvement Case Study Symposium sponsored by the Central Japan Quality Control Association, the Central Japan Improvement and Proposal Activities Convention sponsored by the Nippon Omni-Management Association, and the Japan Management Association Gathering of Frontline Supervisors. Our hope was that they might be useful in future activities.
Quality-Related Education
Strengthening Quality-Related Education
The NGK Group aims to provide customers with products and services at a quality that exceeds expectations. Hence, we are continually working to improve the quality-related education that is given to all employees to ensure they are equipped with quality-related skills and greater quality-related awareness.
The primary educational activities include e-learning, classes conducted both online and face-to-face on themes such as level-based training for new and promoted employees, education in a wide range of fields from quality fundamentals to practical application, individual training on the themes of work issues and departmental needs, and basic statistical training to facilitate data utilization in collaboration with the Digital Transformation & Innovation Dept. We believe that training on quality management systems (QMS) involved in improving work quality and reducing quality risks, and reliability training depending on business details are important. And we aim to help employees acquire this experience through role playing and group discussions. We also try to support employment of statistical methods utilizing practical data. In FY2024 we strengthened the following three kinds of training: (1) Utilization of inverse learning through a video-based seminar course in statistical quality control aimed at improving the data analysis capabilities of employees, (2) Why-Why analysis training as a method for analyzing the causes of failures, and (3) Training to raise awareness of product safety within NGK. In FY2020, we began support activities for those taking QC tests, and the number of employees taking advantage of them has surpassed 1,500.
Quality-Related Education in FY2024
| Training name | Number of participants | Objectives and key characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Training | 17 sessions |
|
| QC Methodology Practice | 63 participants |
|
| SQC (Statistical Quality Control) Methods Video-based Seminar | A total of 305 participants |
|
| SQC (Statistical Quality Control) Methods Seminar | A total of 136 participants |
|
| Why-Why Analysis | 73 participants |
|
| Reliability Basics Training | Reliability Basics Training 1: 64 participants |
|
| Reliability Basics Training 2: 54 participants |
|
|
| Study of Failure and Methodology of Creation | Analysis training session: 88 participants Training course: A total of 16 participants |
|
| QMS Training | ISO/IATF standards interpretation: 852 participants |
|
| ISO/IATF Internal Quality Auditor training: 201 participants |
|
|
| VDA 6.3 Process Auditing Seminar: 38 participants |
|
|
| Product Safety Training | 103 participants |
|
Raising the Level of Autonomous Maintenance Activities
With the aim of achieving a higher standard for maintenance activities and of improving productivity, a number of NGK Group employees in FY2024 took on the challenge of the Autonomous Maintenance Certification Exam (Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance). This qualification is given to those who possess a broad range of necessary knowledge and skills concerning quality management, safety, and machinery maintenance, and are recognized as having the ability to plan and implement autonomous maintenance activities and provide instruction.
The NGK Group will continue encouraging employees to take the Autonomous Maintenance Certification Exam as well as cultivate autonomous maintenance activities and stimulate greater employee motivation.
Voluntary maintenance activities: Activities which have the personnel who use the equipment perform their own preventative measures to maintain equipment condition and safety
Number of Employees Who Passed the Self-Maintenance Expert Test
| Company name | Number of Level 1 examinees | Number of employees who passed Level 1 (pass rate) | Number of Level 2 examinees | Number of employees who passed Level 2 (pass rate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGK | 29 | 15 (52%) | 44 | 32 (73%) |
| NGK CERAMIC DEVICE | 18 | 6 (33%) | 74 | 53 (72%) |
| NGK ELECTRONICS DEVICES | 27 | 14 (52%) | - | - |
