Sustainability
Risk Management
Risk Governance
Basic Approach
The NGK Group addresses the issue of serious risk by empowering various committees to facilitate risk avoidance and prevention, in accordance with the Basic Rules of Crisis Management. Additionally, in the event of some particularly significant risk, the Vice President responsible for the Corporate Planning Office can call a meeting, which would include the president, to develop countermeasures.
In times of increasing socio-economic uncertainty, it is important to have a heightened awareness of risk and to act before risks turn into crises. Therefore, we have established a system whereby the Compliance Committee, Environment, Safety & Health Committee, Quality Committee, HR Committee, and Disaster Prevention and Control Headquarters constantly manage risks while also enabling prompt actions under top management when risks escalate.
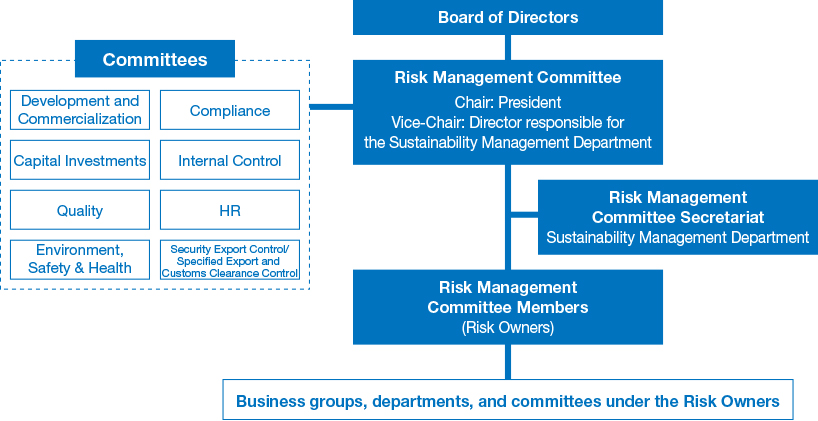
In FY2022, we examined building a company-wide risk management system. Starting from FY2023, we have newly established the Risk Management Committee to comprehensively handle the Group’s risk issues. Our Board of Directors also supervises the activities of the Risk Management Committee by having it report its activities to the Board of Directors at least once a year. Moreover, this risk management system is operated independently of the Audit & Supervisory Board.
Risk Management Framework
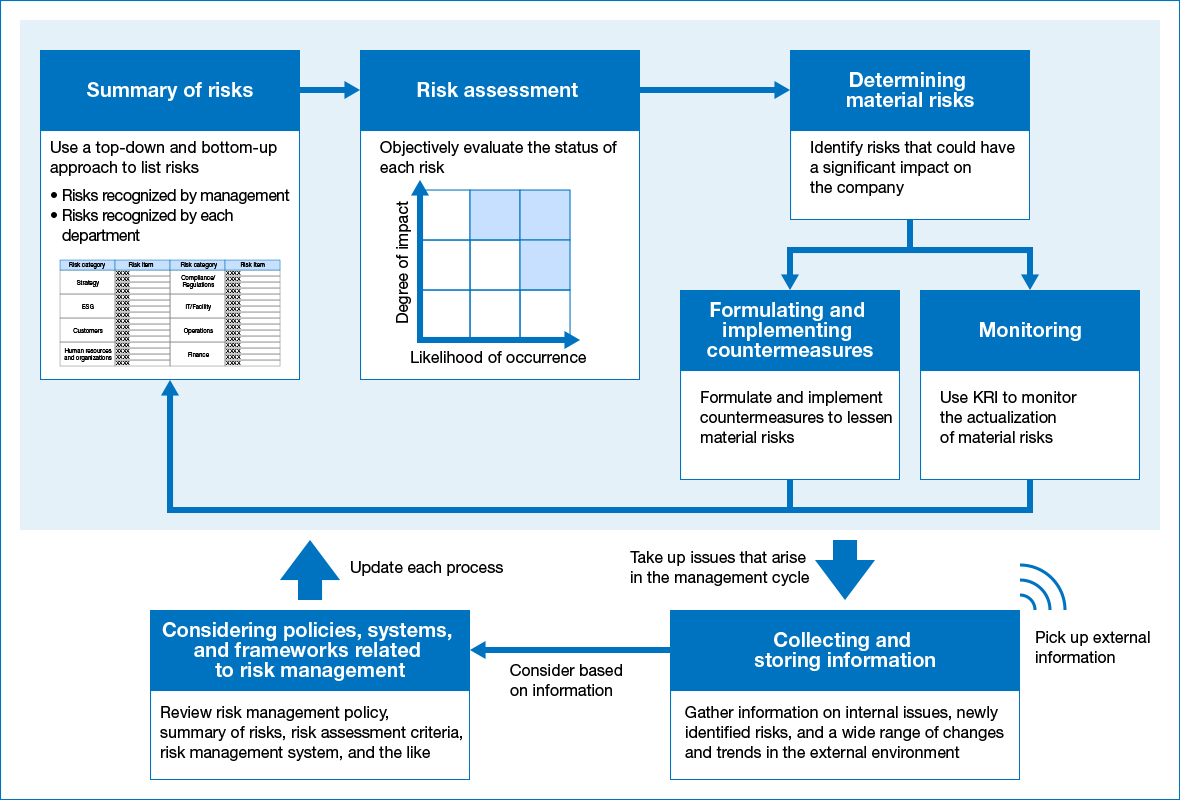
Risk Identification Process
All risks discovered through the standard risk management process, which have the potential to affect the operational or financial situation of the Group are collected, reevaluated, and serious risks were identified in FY2019. The ESG Committee (former name in 2019) then deliberated and designated which identified risks need to be managed by the Group as a whole.
In FY2023, we will strengthen the sustainability of our overall management with the risk management process. This includes conducting risk analysis and assessment based on changes in the internal and external environment, identifying material risks to be managed, and implementing measures and monitoring the progress in addressing these risks under the Risk Management Committee.
Risks, Risk Summaries, Risk Responses
| Risks | Summary | Response |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Business operation risks | All operations | |
|
|
|
| (1) Environment Business | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (2) Digital Society Business | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (3) Energy & Industry Business | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2. R&D-related risks |
|
|
| 3. Legal compliance, human rights and safety, and quality-related risks | (1) Legal compliance-related risks | |
|
|
|
| (2) Human rights and safety-related risks | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (3) Quality-related risks | ||
|
|
|
| 4. Information systems-related risks |
|
|
| 5. Currency exchange, capital, and procurement-related risks |
|
|
| 6. Materials procurement and supply chain risks |
|
|
|
|
|
| 7. Climate change and disaster-related risks |
|
|
|
|
|
Legal Risk Management in Overseas Subsidiaries
The NGK Group is working on understanding better legal risk management by overseas subsidiaries to minimize risks which become global and varied due to overseas business expansion.
We ask all overseas subsidiaries to report information pertaining to the status of lawsuits, legal affairs and consultation with lawyers twice a year, and whistleblowing system usage, export controls and access to legal-related information once a year. Major issues mentioned in such reports are reported to and shared at the Compliance Committee. Consultations from overseas subsidiaries are handled by the legal department and by lawyers, if necessary, to avoid risks.
Identifying and Preventing Risks Based on Questionnaire
As part of efforts to enhance risk management practices, in FY2022 NGK and its Group companies in Japan conducted the fourth CRS (Corporate Risk Survey).
Combining the previously administered CSA (Control Self-Assessment) questionnaire and the compliance awareness survey, the CRS checks the understanding of respondents regarding the possibility of risk and its implications with the goal of grasping and preventing various potential risks arising from daily business operations. Based on the results of the survey, the relevant departments and departments formulate and implement measures to reduce risks.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Initiatives
At NGK, we have established the BCP Countermeasures Headquarters under the direction of the president as an organization to carry out operation and maintenance of our business continuity plan, with the aim of respecting human life and cooperating with the local community. It promotes our business continuity plan (BCP) throughout the entire NGK Group. Measures taken in preparation for putting our BCP into operation include the establishment of multiple manufacturing bases and procurement sources, damage mitigation measures related to buildings and equipment, and employee safety assurance. We also conduct emergency drills presuming a major disaster with the aim of enhancing our ability to cope with a crisis in the event a disaster occurs. During these drills, participants are instructed to take real action according to the plan. This helps us to identify even small issues with each process and procedure and use our findings to improve the BCP. In addition, the BCP Secretariat leads the way in working to ensure business continuity by collecting information early on and implementing countermeasures in response to procurement difficulties stemming from the spread of infectious disease or changes in the global situation.
BCP Organizational Structure
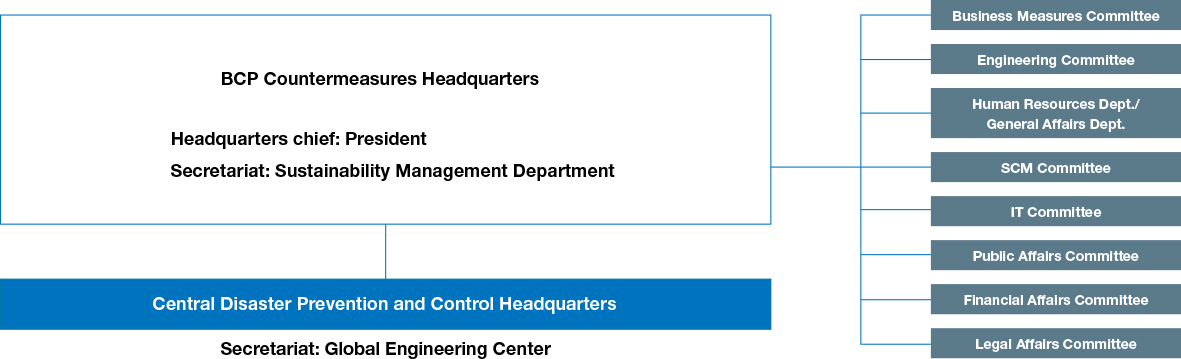
In the event of an emergency or disaster, the Central Disaster Prevention and Control Headquarters will switch over to the Central Disaster Control Headquarters to respond to the disaster.
FY2022 Initiatives
Education |
|
|---|---|
Awareness |
|
Training |
|
Other |
|
Future Initiatives
- Improve the effectiveness of BCP by raising the level of training further (e.g., hold BCP training for operational units)
- Ongoing practical BCP training
- Ongoing support for home disaster prevention initiatives (dealing with those who are unable to return home after a disaster and providing drills for returning home in an emergency, etc.) from the perspective of respect for human life, which is the top priority of BCP
